Props and State
Review, Research, and Discussion
- Does a deployed React application require a server?
- Don’t necessarily needed.
- Why do we prefer to test a React application at the behavior rather than the unit level?
- By testing behavior, you won’t have to adjust after each minor code change.
- What does npm run build do?
-
will create an optimized build of your app in the build folder.
- Describe the actual composition / architecture of a React application
- React application is split into components, it is important that you can add functionality to a component without causing rippling changes through the codebase.
Vocabulary Terms
BDD :
- behavior driven development, a branch of Test Driven Development (TDD), which uses human-readable descriptions of software user requirements as the basis for software tests.
Acceptance Tests :
- testing technique performed to determine whether or not the software system has met the requirement specifications.
mounting :
- the operating system makes files and directories on a storage device available for users to access via the computer’s file system.
build:
- process of converting source code files into standalone software artifacts that can be run on a computer.
setState

- Update to a component state should be done using
setState(). - Pass a function when you can to update state multiple times.
Handling Events
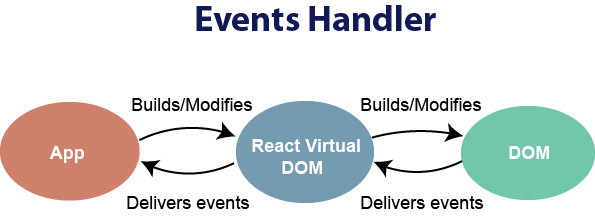
- is very similar to handling events on DOM elements.
- the main defiriens is React events are named using camelCase rather than just lowercase, and with JSX you pass a function as the event handler rather than a string.
- you must call
preventDefaultexplicitly.
Forms
- HTML form elements work a little bit differently from other DOM elements in React, because form elements naturally keep some internal state.
- In React, mutable state is typically kept in the state property of components, and only updated with setState() not like the HTML bacis form.
State and Lifecycle
- Each component in React has a lifecycle which you can monitor and manipulate during its three main phases. The three phases are: Mounting, Updating, and Unmounting.
- You can think of React lifecycle methods as the series of events that happen from the birth of a React component to its death.
setState()in only these React lifecycle methods:componentDidMount,componentDidUpdateandcomponentWillReceiveProps.
Components and Props
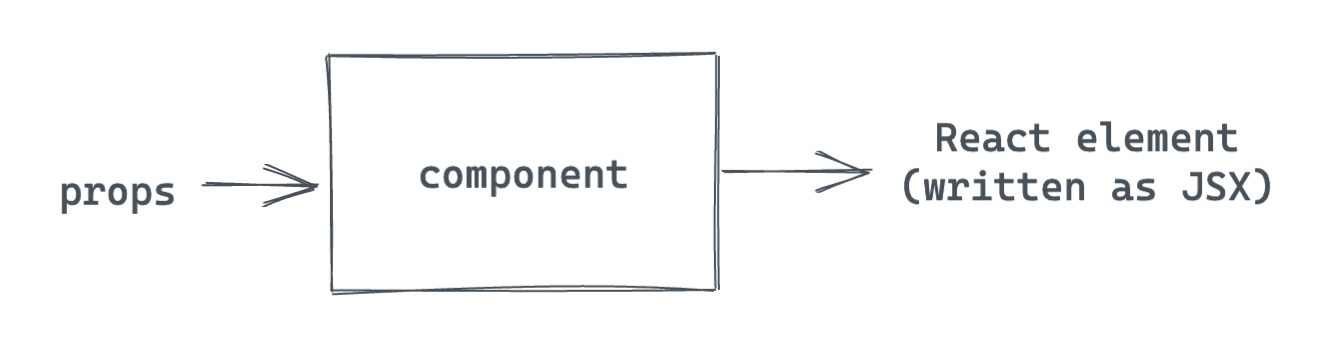
- Components let you split the UI into independent, reusable pieces, and think about each piece in isolation
- Conceptually, components are like JavaScript functions. They accept arbitrary inputs (called “props”) and return React elements describing what should appear on the screen.
- Components can refer to other components in their output
- Whether you declare a component as a function or a class, it must never modify its own props
- All React components must act like pure functions (do not attempt to change their inputs and always return the same result for the same inputs) with respect to their props