AWS: Events
Review, Research, and Discussion
- Describe the similarities between AWS API Gateway + Lambda functions and an ExpressJS Server?
- ExpressJS Server can sit at the heart of any microservices architecture, regardless of what language or platform you’re using. Express Gateway secures your microservices and exposes them through APIs using Node.js, ExpressJS and Express middleware.
- AWS API Gateway a fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale.
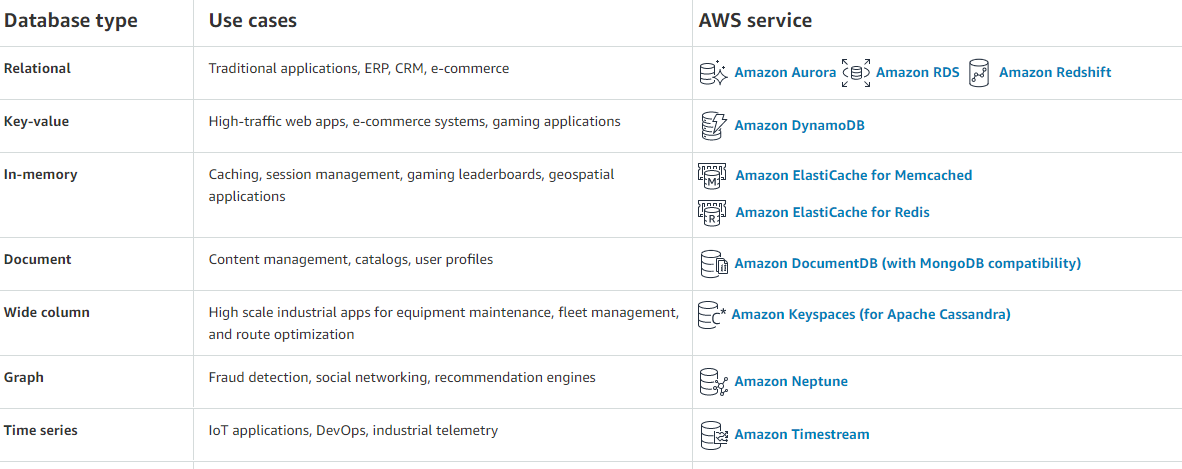
- List the AWS Database offerings and talk about the pros and cons of each?
- mazon Aurora, Amazon Relational Database Service, Amazon Redshift, Key-value Database ,Amazon DynamoDBm In-memory Database , Amazon ElastiCache for Memcached.
- What’s the difference between a FIFO and a standard queue?
- A standard queue tries to preserve the order of messages (best-effort), but there is a possibility of a message being delivered out of order. In a FIFO queue, messages are grouped into “Message groups” and all messages within a message group are sent and received in strict order.
-
How can the server be assured a message was properly received?
- By having the client emit a “received” event back to the server upon receipt of the message.
Vocabulary Terms
Serverless API :
- using API Gateway you can create RESTful APIs that enable real-time two-way communication applications, API Gateway supports containerzied and serverless workloads as well as web applications.
Triggers :
- an AWS Lambda resource or resource in another service that you configure to invoke your function in response to lifecycle events, external requests or on a schedule, a function can have multiple triggers.
Dynamo vs Mongo :
- Mongo can be deployed anywhere, Dynamo is only available on AWS
- Mongo is JSON based document store, Dynamo is limited key-value store with JSON support
- Mongo is rich query language, Dynamo is key-value queries.
Dynamoose vs Mongoose:
- Dynamoose is a DynamoDB API structured like Mongoose, lets us provide a schema and perform CRUD operations against a DynamoDB table, installed via node and configured based on role.
AWS — SQS and SNS


SQS - Simple queue service
- Distributed queuing system
- Messages are not pushed to receivers, receivers have to poll SQS to receive messages
- Messages can’t be received by multiple receivers at the same time
- Any one receiver can receive a message, process and delete it, other receivers do not receive the same message later
- Mainly used to decouple applications or integrate applications
- Messages can be stored in SQS for short duration of time (max 14 days)
SNS - Simple notification service
- Fast, flexible and fully managed push notification service that lets you send individual messages or bulk messages
- Distributed publish/subscribe system
- Messages are pushed to subscribers as and when they are sent by publishers to SNS
- SNS supports several end points such as email, sms, http end point and SQS
- If you want unknown number and type of subscribers to receive messages, you need SNS