Sending Form Data
- Once the form data has been validated on the client-side, it is okay to submit the form.
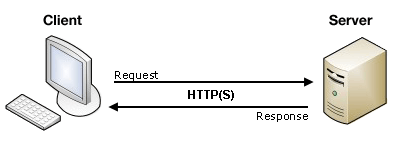
Client/server architecture
- The web uses a client/server architecture that can be summarized as follows. a client sends a request to a server , using the HTTP protocol. The server answers the request using the same protocol.
-
An HTML form on a web page is nothing more than a convenient user-friendly way to configure an HTTP request to send data to a server. This enables the user to provide information to be delivered in the HTTP request.
- The
<form>element defines how the data will be sent. All of its attributes are designed to let you configure the request to be sent when a user hits a submit button. The two most important attributes are action and method. - The action attribute defines where the data gets sent.
- The method attribute defines how data is sent.
- The
HTTPprotocol provides several ways to perform a request; HTML form data can be transmitted via a number of different methods, the most common being theGETmethod and thePOSTmethod. - The
GETmethod is the method used by the browser to ask the server to send back a given resource. - The
POSTmethod It’s the method the browser uses to talk to the server when asking for a response that takes into account the data provided in the body of the HTTP request. - Whichever HTTP method you choose, the server receives a string that will be parsed in order to get the data as a list of key/value pairs.
- Sending files with HTML forms is a special case.
- Files are binary data — or considered as such — whereas all other data is text data.
- Because HTTP is a text protocol, there are special requirements for handling binary data.
- This attribute lets you specify the value of the
Content-TypeHTTP header included in the request generated when the form is submitted. - This header is very important because it tells the server what kind of data is being sent. By default, its value is
application/x-www-form-urlencoded.