Access Control (ACL)
Review, Research, and Discussion
- When is Basic Authorization used vs. Bearer Authorization?
-
The Basic authentication schemes are dedicated to the authentication using a username and a secret.
-
The Bearer authentication scheme is dedicated to the authentication using a token even if this scheme comes from an OAuth2 specification, you can still use it in any other context where tokens are exchange between a client and a server.
-
- What does the JSON Web Token package do?
- used to send information that can be verified and trusted by means of a digital signature.
- What considerations should we make when creating and storing a SECRET?
- Use encryption to store secrets within .git repositories.
- Use environment variables.
- Use “Secrets as a service” solutions.
Vocabulary Terms
encryption :
- securing data by encoding it mathematically .
token :
- is a secure format used to transmit sensitive information between two services .
bearer :
- is an HTTP authentication scheme originally created as part of OAuth 2.0, but is now used on its own.
secret :
- a key that is added when generating the token as part of it to scure it more.
JSON Web Token :
- A token used for authentication, consists of a header, a payload and a signature.
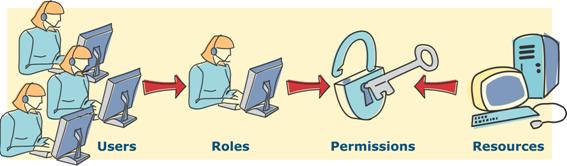
RBAC

- Is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users.
- Can implement mandatory access control (MAC) or discretionary access control (DAC).
-
a policy-neutral access-control mechanism defined around roles and privileges.
-
Three primary rules are defined for RBAC:
- Role assignment: A subject can exercise a permission only if the subject has selected or been assigned a role.
- Role authorization: A subject’s active role must be authorized for the subject. With rule 1 above, this rule ensures that users can take on only roles for which they are authorized.
- Permission authorization: A subject can exercise a permission only if the permission is authorized for the subject’s active role. With rules 1 and 2, this rule ensures that users can exercise only permissions for which they are authorized.
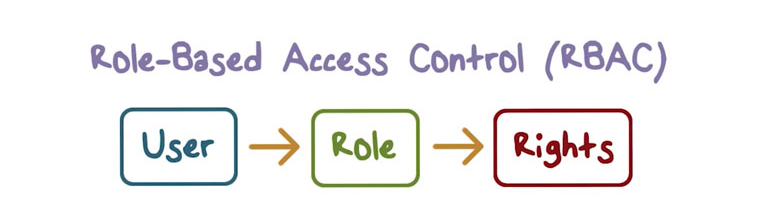
When defining an RBAC model, the following conventions are useful:
- S = Subject = A person or automated agent
- R = Role = Job function or title which defines an authority level
- P = Permissions = An approval of a mode of access to a resource
- SE = Session = A mapping involving S, R and/or P
- SA = Subject Assignment
- PA = Permission Assignment
- RH = Partially ordered Role Hierarchy. RH can also be written: ≥ (The notation: x ≥ y means that x inherits the permissions of y.)
- A subject can have multiple roles.
- A role can have multiple subjects.
- A role can have many permissions.
- A permission can be assigned to many roles.
- An operation can be assigned to many permissions.
- A permission can be assigned to many operations.

Comparing with ACL
- RBAC differs from access control lists (ACLs), used in traditional discretionary access-control systems, in that RBAC systems assign permissions to specific operations with meaning in the organization, rather than to low-level data objects.