Defintion of REST

-
s a software architectural style which uses a subset of HTTP.
- It is commonly used to create interactive applications that use Web services.
- A Web service that follows these guidelines is called RESTful.
SuperAgent

- SuperAgent is light-weight progressive ajax API crafted for flexibility, readability, and a low learning curve after being frustrated with many of the existing request APIs. It also works with Node.js! .
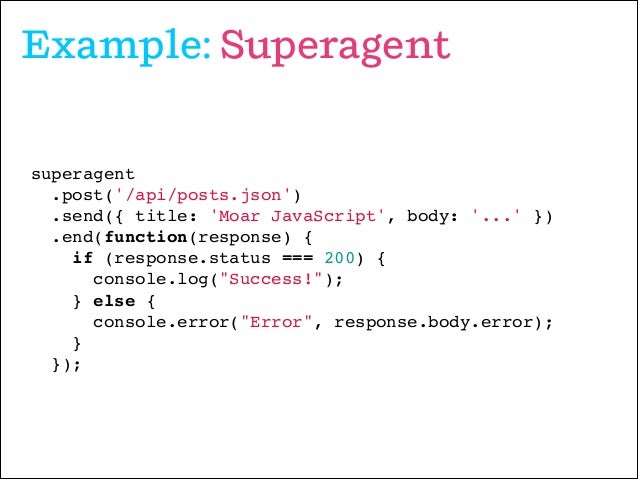
Request basics
- A request can be initiated by invoking the appropriate method on the request object, then calling
.then()(or.end()orawait) to send the request. - Old-style callbacks are also supported, but not recommended. Instead of
.then()you can call.end():. DELETE,HEAD,PATCH,POST, andPUTrequests can also be used,DELETEcan be also called as.del()for compatibility with old IE where delete is a reserved word.
GET requests
- The
.query()method accepts objects, which when used with the GET method will form a query-string.Query strings
req.query(obj)is a method which may be used to build up a query-string. For example populating?format=json&dest=/loginon aPOST.
TLS options
-
In Node.js SuperAgent supports methods to configure HTTPS requests:
.ca(): Set the CA certificate(s) to trust..cert(): Set the client certificate chain(s)..key(): Set the client private key(s)..pfx(): Set the client PFX or PKCS12 encoded private key and certificate chain..disableTLSCerts(): Does not reject expired or invalid TLS certs.
Parsing response bodies
- SuperAgent will parse known response-body data for you, currently supporting application/x-www-form-urlencoded, application/json, and multipart/form-data.
Aborting requests
- To abort requests simply invoke the
req.abort()method.Authentication
- In both Node and browsers auth available via the
.auth()
Browser and node versions
- SuperAgent has two implementations: one for web browsers (using XHR) and one for Node.JS (using core http module).
-
By default Browserify and WebPack will pick the browser version.
- If want to use WebPack to compile code for Node.JS, you must specify node target in its configuration.