Linked Lists
What is a linked list?
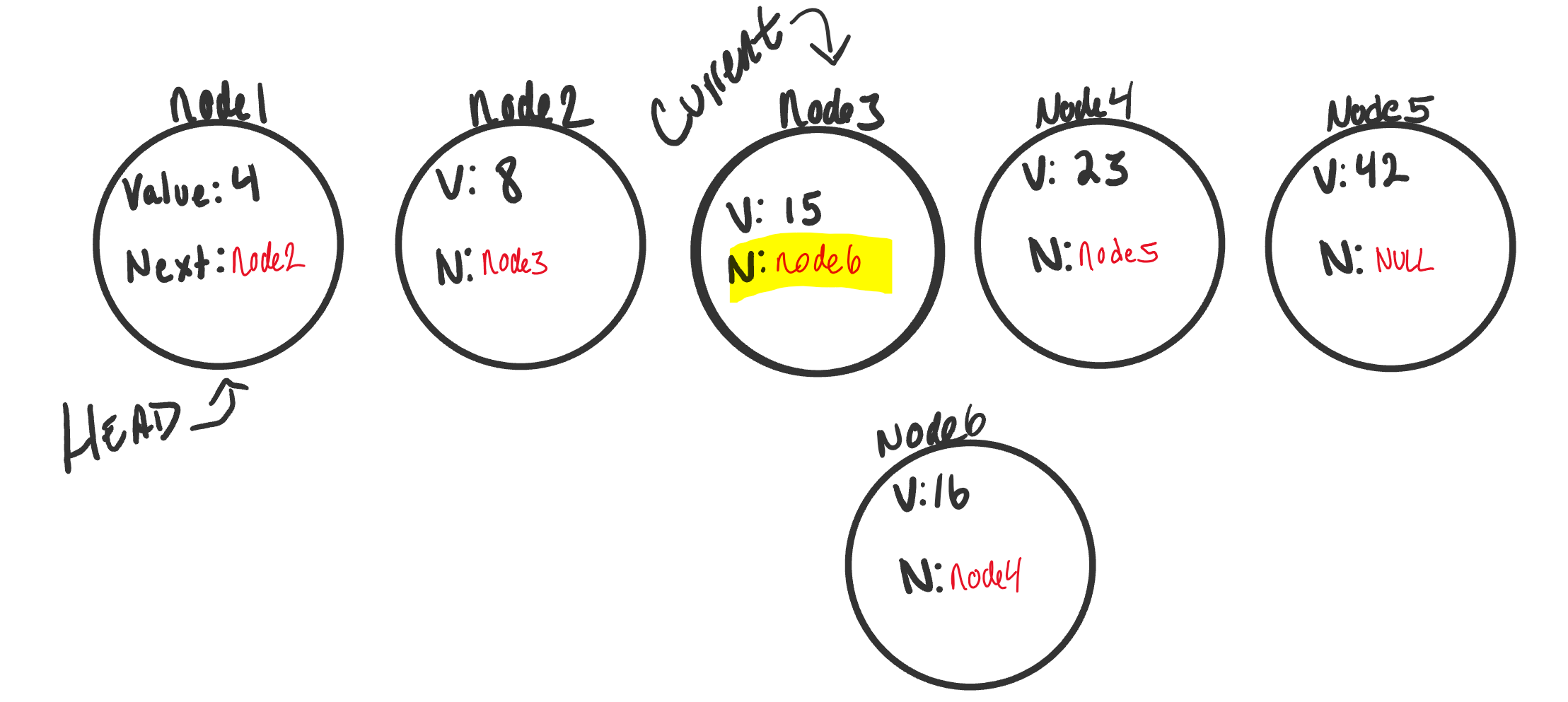
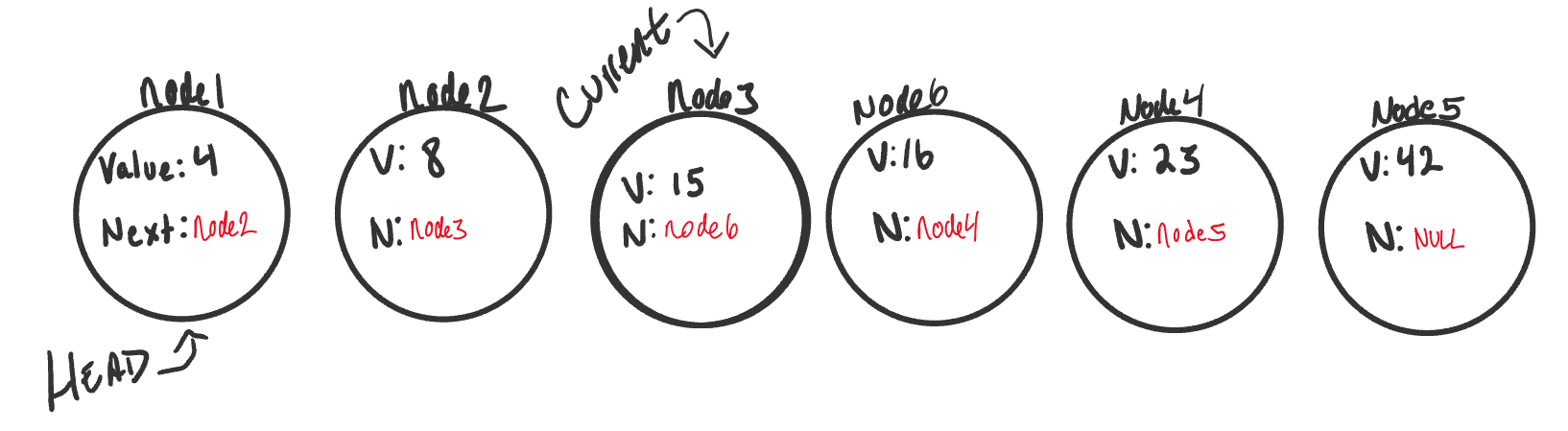
- A linked list is an ordered collection of data elements. A data element can be represented as a node in a linked list.
- Each node consists of two parts: data & pointer to the next node.
- nodes are linked using pointers.
A linked list has the following properties:
- Successive nodes are connected by pointers.
- The last node points to null.
- A head pointer is maintained which points to the first node of the list.
- A linked list can grow and shrink in size during execution of the program.
- It can be made just as long as required.
- It allocates memory as the list grows..

advantage of a linked list
- In contrast to an array, which stores data contiguously in memory, a linked list can easily insert or remove nodes from the list without reorganization of the entire data structure.
Types of Linked lists
There are a few different types of linked lists. But the most popular ones are: singly, doubly and circular.

- We depend on the
Nextvalue in each node to guide us where the next reference is pointing. - The best way to approach a traversal is through the use of a
while()loop.Adding a Node