Images & Coloers & Text
Images
-
Images can be used to set the tone for a site in less time than it takes to read a description.
-
To add an image into the page you need to use an
<img>element. - it carry the following two attributes:
- src :This tells the browser where it can find the image file.
- alt :This provides a text description of the image which describes the image if you cannot see it.
- You will also often see an
<img>element use two other attributes that specify its size:- height :This specifies the height of the image in pixels.
- width :This specifies the width of the image in pixels.
-
Images created for the web should be saved at a resolution of 72 ppi. The higher the resolution of the image, the larger the size of the file.
<figure>element to contain images and their caption so that the two are associated.
Color :
Color not only brings your site to life, but also helps convey the mood and evokes reactions
-
The color property allows you to specify the color of text inside an element.
-
You can specify any color in CSS in one of three ways:
-
rgb values : These express colors in terms of how much red, green and blue are used to make it up. For example: rgb(100,100,90).
-
hex codes : These are six-digit codes that represent the amount of red, green and blue in a color, preceded by a pound or hash #sign. For example: #ee3e80.
-
color names : There are 147 predefined color names that are recognized by browsers. For example: DarkCyan.
-
#### * Color pickers can help you find the color you want.
#### * It is important to ensure that there is enough contrast between any text and the background color (otherwise people will not be able to read your content).
#### * CSS3 has introduced an extra value for RGB colors to indicate opacity. It is known as RGBA.
#### * CSS3 also allows you to specify colors as HSL values, with an optional opacity value. It is known as HSLA.
Text :
- The properties that allow you to control the appearance of text can be split into
two groups:
- Those that directly affect the font and its appearance.
- Those that would have the same effect on text no matter what font you were using.
-
Typeface Terminology :
-
Serif : Serif fonts have extra details on the ends of the main strokes of the letters. These details are known as serifs.
-
Sans-Serif : Sans-serif fonts have straight ends to letters.
-
Monospace : Every letter in a monospace font is the same width.
-
Weight : The font weight not only adds emphasis but can also affect the amount of white space and contrast on a page.
-
Style : Italic fonts have a cursive aspect to some of the lettering.
-
Stretch : In condensed (or narrow) versions of the font, letters are thinner and closer together. In expanded versions they are thicker and further apart.
-
The font-size property enables you to specify a size for the font.
-
@font-faceallows you to use a font, even if it is not installed on the computer of the person browsing. - The font-weight property allows you to create bold text.
There are two values that this property commonly takes:
- normal : This causes text to appear at a normal weight.
- bold : This causes text to appear bold.
- If you want to create italic text, you can use the font-style
property. There are three values this property can take:
- normal: This causes text to appear in a normal style.
- italic: This causes text to appear italic.
- oblique: This causes text to appear oblique.
- The text-transform property is used to change the case of text giving it
one of the following values:
- uppercase: This causes the text to appear uppercase.
- lowercase: This causes the text to appear lowercase.
- capitalize: This causes the first letter of each word to appear capitalized.
- The text-decoration property allows you to specify the following values:
- none: This removes any decoration already applied to the text.
- underline: This adds a line underneath the text.
- overline: This adds a line over the top of the text.
- line-through: This adds a line through words.
- blink: This animates the text to make it flash on and off.
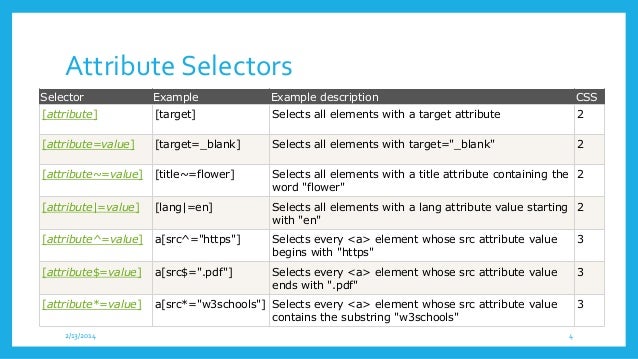
- Attribute Selectors: